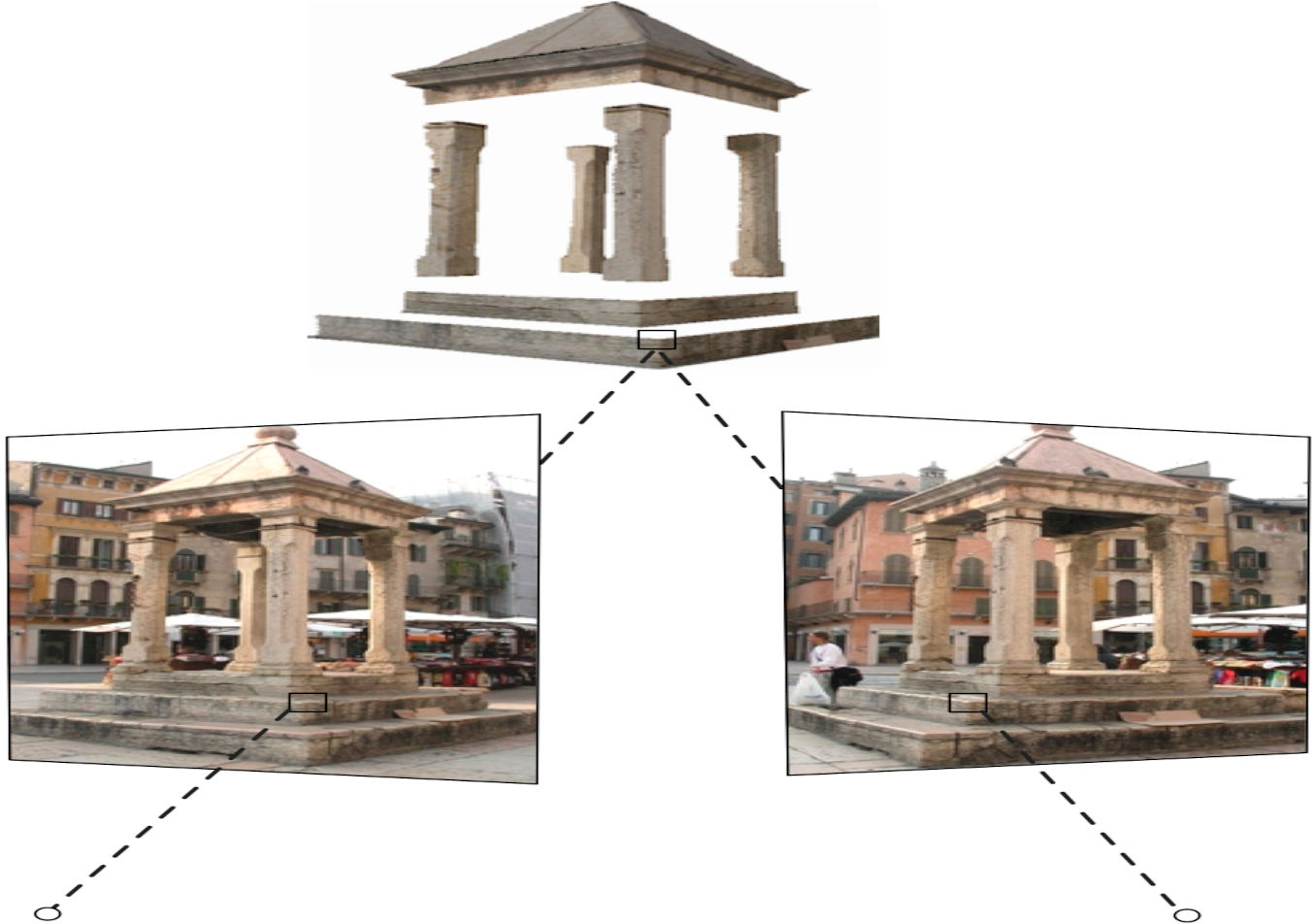
\In this project I finalize my two-view-geometry project with 3D point clouds from the two viewpoint images. The complete code can be found at two-view-geometry.py in this repo.
import os
import sys
import cv2
import _pickle as pickle
#import cPickle as pickle
import math
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inlinefrom utils import *
src_image_path = "./imgs/0001.png"
dst_image_path = "./imgs/0002.png"
src_image = cv2.imread(src_image_path, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
dst_image = cv2.imread(dst_image_path, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)Lets observe the 2 view images:
#https://documents.epfl.ch/groups/c/cv/cvlab-unit/www/data/multiview/modelFountain.html
ff, axs = plt.subplots(2,1,figsize=(15,15))
#opncv is bgr vs rgb
plt.subplot(121),plt.imshow(src_image.T[[2,1,0]].T)
plt.subplot(122),plt.imshow(dst_image.T[[2,1,0]].T)
plt.show()Lets import everything from the previous project:
MIN_MATCH_COUNT = 10
src_gray = cv2.cvtColor(src_image , cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
dst_gray = cv2.cvtColor(dst_image , cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
kp1, desc1 = computeDescriptions(src_gray, "feats/{}_feats.kp".format(os.path.basename(src_image_path).split(".")[0]))
kp2, desc2 = computeDescriptions(dst_gray, "feats/{}_feats.kp".format(os.path.basename(dst_image_path).split(".")[0]))
matcher = genMatcher()
knn_matches = matcher.knnMatch(desc1, desc2, 2)
#-- Filter matches using the Lowe's ratio test
ratio_thresh = 0.8
good = []
pts1 = []
pts2 = []
for m,n in knn_matches:
if m.distance < ratio_thresh * n.distance:
good.append(m)
pts2.append(kp2[m.trainIdx].pt)
pts1.append(kp1[m.queryIdx].pt)
if len(good) <= MIN_MATCH_COUNT:
print( "Not enough matches are found - {}/{}".format(len(good), MIN_MATCH_COUNT) )
matchesMask = None
#src_pts = np.int32([ kp1[m.queryIdx].pt for m in good ])
#dst_pts = np.int32([ kp2[m.trainIdx].pt for m in good ])
pts1 = np.int32(pts1)
pts2 = np.int32(pts2)
F, mask = cv2.findFundamentalMat(pts1, pts2, cv2.FM_RANSAC ) #FM_LMEDS
# We select only inlier points
pts1 = pts1[mask.ravel()==1]
pts2 = pts2[mask.ravel()==1]Here we load the intrinsics and distortion coefficients
K = np.loadtxt('./calib.txt')
#dist = np.loadtxt('./distortions.txt')Lets get the possilbe rotation matrices as decompostion of the Essential ( HZ (9.12) )
Kinv = np.linalg.inv(K)
"""Pose for 1st view"""
P0 = np.eye(3,4)
""""E = K.T * F * K"""
E = np.matmul( K.T , np.matmul( F, K ) )R1, R2, t = decompEssentialMatrix(E)print(R1)array([[ 0.77661096, -0.07634356, -0.62533757],
[-0.05441777, -0.99704934, 0.05414173],
[-0.62762579, -0.00801758, -0.77847389]])
print(R2)array([[ 0.99373088, 0.0071714 , -0.11156838],
[-0.01026916, 0.99957683, -0.02721575],
[ 0.11132599, 0.02819085, 0.99338401]])
print(t)array([ 0.95941719, -0.03505637, -0.27980297])
Lets compare our decomposition with Cv2 recover pose:
retval, R_, t_, mask = cv2.recoverPose(E, pts1, pts2, K)print(t_)array([[ 0.95941719],
[-0.03505637],
[-0.27980297]])
print(R_)array([[ 0.99373088, 0.0071714 , -0.11156838],
[-0.01026916, 0.99957683, -0.02721575],
[ 0.11132599, 0.02819085, 0.99338401]])
Ok, they are identical. CV2 recover pose takes chirality solution into account and gave us R=R2.
Btw, for our naive implemetaton, there are 4 possible solutions based on chirality contraints. (HZ (9.14)). This is automated in the final solution two_view_geometry.py based on minimum reprojection error.
P1 = np.column_stack( [ R1, t ] )
P2 = np.column_stack( [ R2, t ] )
P3 = np.column_stack( [ R1, -t ] )
P4 = np.column_stack( [ R2, -t ] )The following are the 3d-2d transformations and reprojection error functions based on (HZ (9.12))
def getNormalizedCoordinates(a, kinv):
#converts 2x1 array to normalized (3x1) coordinates
a_hg = np.array([a[0],a[1],1])
a_calib = np.matmul(kinv, a_hg)
return a_calib
def getVectorCrossMatrix(a):
#converts a 3x1 vector to 3x3 cross product matrix
a_cross = np.zeros((3,3))
a_cross[0,1] = -a[2]
a_cross[0,2] = a[1]
a_cross[1,0] = a[2]
a_cross[1,2] = -a[0]
a_cross[2,0] = -a[1]
a_cross[2,1] = a[0]
return a_cross
#https://perception.inrialpes.fr/Publications/1997/HS97/HartleySturm-cviu97.pdf
def LinearLSTriangulation( u, P, u1, P1, mode=0):
u_cross = getVectorCrossMatrix(u)
u1_cross = getVectorCrossMatrix(u1)
A0 = np.matmul(u_cross,P)
A1 = np.matmul( u1_cross, P1 )
A_full = np.concatenate([A0, A1])
#A_full = A_full[[0,1,3,4],:]
A = A_full[:,:-1]
B = -A_full[:,-1]
#print(A,B)
if mode == 0:
X = np.linalg.lstsq(A,B,rcond=-1)
#print(X)
X = np.array( [ X[0][0], X[0][1], X[0][2], 1 ] )
else:
X = cv2.solve(A, B, flags=cv2.DECOMP_SVD)
#print(X)
X = np.array( [ X[1][0][0], X[1][1][0], X[1][2][0], 1 ] )
return X
def get3DReprojectionError(X, K, P, x):
KP = np.matmul( K, P)
x_uv = np.matmul(KP, X)
x_uv_inhg = np.array( [x_uv[0]/x_uv[2], x_uv[1]/x_uv[2] ] )
return np.linalg.norm(x_uv_inhg - x)
def TriangulatePoints( ptsa, ptsb, K, Kinv, Pa, Pb ):
ptcloud = []
reprojection_errs = []
for a,b in zip(ptsa, ptsb):
ua = getNormalizedCoordinates( a , Kinv )
ub = getNormalizedCoordinates( b , Kinv )
X = LinearLSTriangulation( ua, Pa, ub, Pb )
err = get3DReprojectionError(X, K, Pb, b )
ptcloud.append(X)
reprojection_errs.append(err)
print( "Mean Reprojection error:", np.array(reprojection_errs).mean() )
return np.array(ptcloud)#P1 is unity rotation and 0 translation
P = np.eye(3,4)Kinv = np.linalg.inv(K)print(Kinv)array([[ 3.62387116e-04, 0.00000000e+00, -5.51078464e-01],
[ 0.00000000e+00, 3.61773559e-04, -3.64237237e-01],
[ 0.00000000e+00, 0.00000000e+00, 1.00000000e+00]])
Here are the computed 3d points from triangulation function above:
pts3d = TriangulatePoints( pts1, pts2, K, Kinv, P, P2 )Mean Reprojection error: 0.9033128555260254
fig = plt.figure()
ax = plt.axes(projection='3d')
ax.scatter3D(pts3d[:,0],pts3d[:,1],pts3d[:,2])Lets write the p3d to output .ply
#https://github.com/opencv/opencv/blob/master/samples/python/stereo_match.py
ply_header = '''ply
format ascii 1.0
element vertex %(vert_num)d
property float x
property float y
property float z
property uchar red
property uchar green
property uchar blue
end_header
'''
def write_ply(fn, verts, colors):
verts = verts.reshape(-1, 3)
colors = colors.reshape(-1, 3)
verts = np.hstack([verts, colors])
with open(fn, 'wb') as f:
f.write((ply_header % dict(vert_num=len(verts))).encode('utf-8'))
np.savetxt(f, verts, fmt='%f %f %f %d %d %d ')out_pts = np.array([ [pts[0],pts[1],pts[2]] for pts in pts3d ])
out_colors = np.array([ src_image[pt[1],pt[0]] for pt in pts2 ])
#opncv is bgr vs rgb
write_ply("./out.ply", out_pts, out_colors.T[[2,1,0]].T)References
Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision (second edition), R.I. Hartley and A. Zisserman, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-54051-8